Algorithmus von Dijkstra
Der Algorithmus von Dijkstra (nach seinem Erfinder Edsger W. Dijkstra) dient der Berechnung eines kürzesten Pfades zwischen einem Startknoten und einem beliebigen Knoten in einem kantengewichteten Graphen. Die Gewichte dürfen dabei nicht negativ sein. Für Graphen mit negativen Gewichten aber ohne negative Zyklen ist der Bellman-Ford-Algorithmus geeignet.
Für nicht zusammenhängende, ungerichtete Graphen kann der Abstand zu bestimmten Knoten auch unendlich sein, wenn ein Pfad zwischen Startknoten und diesen Knoten nicht existiert. Dasselbe gilt auch für gerichtete, nicht stark zusammenhängende Graphen.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Algorithmus
G bezeichnet den gewichteten Graphen mit V (engl. vertex) als Knotenmenge, E (engl. edge) als Kantenmenge und Kosten als Gewichtsfunktion. s ist der Startknoten, U (engl. unvisited) ist die Menge der noch zu bearbeitenden Knoten und z ist ggf. ein spezieller Zielknoten, bei dem abgebrochen werden kann, wenn seine Distanz zum Startknoten bekannt ist.
Nach Ende des Algorithmus enthält Distanz die Abstände aller Knoten zu s. In Vorgänger ist ein spannender Baum der von s aus ausgehenden minimalen Wege in Form eines In-Tree gespeichert.
Wird bei Erreichen von z abgebrochen (mit #optional gekennzeichet), so enthalten Distanz und Vorgänger diese Werte nur für alle zuvor betrachteten Knoten. Dies sind mindestens die, die kleineren Abstand als z zu s besitzen.
01 für jedes v aus V
02 Distanz(v) := unendlich, Vorgänger(v) := kein
03 Distanz(s) := 0, Vorgänger(s) := 'begin', U := V
04 M := EMPTYSET
05 für jedes (s,v) aus E mit v aus U
06 Distanz(v) := Kosten(s,v)
07 M := M UNION {v}
08 Vorgänger(v) := s
09
10 solange M nicht leer
11 wähle u aus M mit Distanz(u) minimal
12 M := M - {u}
13 U := U - {u}
14 wenn u = z dann STOP # optional
15 für jedes (u,v) aus E mit v aus U
16 M := M UNION {v}
17 wenn Distanz(u) + Kosten(u,v) < Distanz(v) dann
18 Distanz(v) := Distanz(u) + Kosten(u,v)
19 Vorgänger(v) := u
Grundlegende Konzepte und Verwandtschaften
Der Algorithmus gehört zur Klasse der Greedy-Algorithmen. Sukzessive wird der nächstbeste Knoten, der einen kürzesten Pfad besitzt (Zeile 06), in eine Ergebnismenge aufgenommen und aus der Menge der noch zu bearbeitenden Knoten entfernt (Zeile 07). Damit findet sich eine Verwandtschaft zur Breitensuche, die ebenfalls solch ein gieriges Verhalten aufweist.
Ein alternativer Algorithmus zur Suche kürzester Pfade, der sich dagegen auf das Optimalitätsprinzip von Bellman stützt, ist der Floyd-Warshall-Algorithmus. Das Optimalitätsprinzip besagt, dass, wenn der kürzeste Pfad von A nach C über B führt, der Teilpfad A B auch der kürzeste Pfad von A nach B sein muss.
Ein weiterer alternativer Algorithmus ist der A*-Algorithmus, der den Algorithmus von Dijkstra um eine Abschätzfunktion erweitert. Falls diese gewisse Eigenschaften erfüllt, kann damit der kürzeste Pfad unter Umständen schneller gefunden werden.
Berechnung eines Spannbaumes
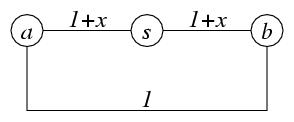
Nach Ende des Algorithmus ist in Vorgänger ein spannender Baum der Komponente von s aus kürzesten Pfaden von s zu allen Knoten der Komponente verzeichnet. Dieser Baum ist jedoch nicht notwendigerweise auch minimal, wie die Abbildung zeigt:
Sei x eine Zahl größer 0. Minimal spannende Bäume sind entweder durch die Kanten {a,s} und {a,b} oder {b,s} und {a,b) gegeben. Die Gesamtkosten eines minimal spannenden Baumes betragen 2+x. Dijkstras Algorithmus liefert mit Startpunkt s die Kanten {a,s} und {b,s} als Ergebnis. Die Gesamtkosten dieses spannenden Baumes betragen 2+2x.
Die Berechnung eines minimalen Spannbaumes ist mit dem Algorithmus von Prim oder dem Algorithmus von Kruskal möglich.
Zeitkomplexität
Im Folgenden sei m die Anzahl der Kanten und n die Anzahl der Knoten. Der Algorithmus von Dijkstra muss n mal den nächsten minimalen Knoten u bestimmen (Zeilen 05 und 06). Eine Möglichkeit wäre jedes Mal diesen mittels Durchlaufen durch eine Knotenliste zu bestimmen. Die Laufzeit beträgt dann <math>O(n^2)</math>. Eine effizientere Möglichkeit zur Liste bietet die Verwendung der Datenstruktur Fibonacci-Heap. Die Laufzeit beträgt dann lediglich <math>O(m+n\cdot\log (n))</math>.
Anwendungen
Routenplaner sind ein prominentes Beispiel, bei dem dieser Algorithmus eingesetzt werden kann. Der Graph repräsentiert hier das Straßennetz, welches verschiedene Punkte miteinander verbindet. Gesucht ist die kürzeste Route zwischen zwei Punkten.
Dijkstras Algorithmus wird auch im Internet als Routing-Algorithmus in OSPF eingesetzt.
Siehe auch
Literatur
- E. W. Dijkstra: A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. In: Numerische Mathematik. 1 (1959), S. 269–271
Weblinks
- Eine lustige Geschichte und eine sehr gute Erklärung
- Ein anschauliches Beispiel
- Java-Demonstration mit selbst erstellten Bäumen
- Dijkstra Algorithmus in C - auf spanisch
- Dijkstra-Algorithmus in C (englisch)
Literatur / Literature
- E. W. Dijkstra: A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. In: Numerische Mathematik. 1 (1959), S. 269–271
- Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest, and Clifford Stein. Introduction to Algorithms, Second Edition. MIT Press and McGraw-Hill, 2001. ISBN 0262032937. Section 24.3: Dijkstra's algorithm, pp.595–601.
Weblinks
- Animation of Dijkstra's algorithm
- The Boost Graph Library (BGL)
- Javascript Dijkstra's Algorithm
- Interactive Implementation of Dijkstra's Algorithm
- Shortest Path Problem: Dijkstra's Algorithm
Code
Implementations in various programming languages of Dijkstra's algorithm.
C
void dodijkstra(int sr,int ds,int path[]) { struct node { int pre; /* Predecessor */ int length; /* Length between the nodes */ enum {perm,tent} label; /* Enumeration for permanent and tentative labels */ }state[MAX]; int i,k,min; struct node *p; /* Initialisation of the nodes aka First step of Dijkstra Algo */ for(p=&state[0];p<&state[no_nodes];p++) { p->pre= -1; p->length=INFTY; p->label=tent; } state[ds].length=0; /* Destination length set to zero */ state[ds].label=perm; /* Destination set to be the permanent node */ k=ds; /* initial working node */ /* Checking for a better path from the node k ? */ do { for(i=0;i<no_nodes;i++) { if(dist[k][i]!=0 && state[i].label==tent) { if((state[k].length+dist[k][i])<state[i].length) { state[i].pre=k; state[i].length=state[k].length+dist[k][i]; } } } k=0; min=INFTY; /* Find a node which is tentatively labeled and with minimum label */ for(i=0;i<no_nodes;i++) { if(state[i].label==tent && state[i].length<min) { min=state[i].length; k=i; } } state[k].label=perm; } while(k!=sr); i=0; k=sr; /* Print the path to the output array */ do {path[i++]=k;k=state[k].pre;} while(k>=0); path[i]=k; }
C++
#include < map> #include <queue> using namespace std; #define X first #define Y second template <class Node, class Edge=int> class Dijkstra { public: Dijkstra() {} Dijkstra(const Node &n, const Edge &e=0) { push(n, e); } bool empty() const { return q.empty(); } void push(const Node &n, const Edge &e=0) { Iter it = m.find(n); if (it == m.end()) it = m.insert(make_pair(n, e)).X; else if (it->Y > e) it->Y = e; else return; q.push(make_pair(e, it)); } const Node &pop() { cur = q.top().Y; do q.pop(); while (!q.empty() && q.top().Y->Y < q.top().X); return cur->X; } const Edge &dist() const { return cur->Y; } void link(const Node &n, const Edge &e=1) { push(n, cur->Y + e); } private: typedef typename map<Node, Edge>::iterator Iter; typedef pair<Edge, Iter> Value; struct Rank : public binary_function<Value, Value, bool> { bool operator()(const Value& x, const Value& y) const { return x.X > y.X; } }; map<Node, Edge> m; priority_queue<Value, vector<Value>, Rank> q; Iter cur; }; // Example usage (nodes and edges are represented with ints) int shortestDistance(int nodes, int startNode, int endNode, int **dists) { Dijkstra<int> dijkstra(startNode); while (!dijkstra.empty()) { int curNode = dijkstra.pop(); if (curNode == endNode) return dijkstra.dist(); for (int i = 0; i < nodes; i++) if (dists[curNode][i] >= 0) // "i" is a neighbor of curNode dijkstra.link(i, dists[curNode][i]); // add weighted edge } return -1; // No path found }
Actionscript
class Dijkstra { private var visited:Array; private var distance:Array; private var previousNode:Array; private var startNode:Number; private var map:Array; private var infiniteDistance:Number; private var numberOfNodes:Number; private var bestPath:Number; private var nodesLeft:Array; public function Dijkstra(ourMap:Array, startNode:Number, infiniteD:Number) { this.infiniteDistance = infiniteD; this.startNode = startNode; this.distance = new Array(); this.previousNode = new Array(); this.visited = new Array(); this.map = ourMap; this.numberOfNodes = this.map[0].length; this.bestPath = 0; this.nodesLeft = new Array(); } private function findShortestPath():Void { for (var i = 0; i < this.numberOfNodes; i++) { if (i == this.startNode) { this.visited[i] = 1; this.distance[i] = 0; } else { this.visited[i] = 0; this.distance[i] = this.map[this.startNode][i]; } this.previousNode[i] = 0; } while(this.somethingLeft(this.visited)) { this.nodesLeft = this.nodesNotVisited(this.visited); this.bestPath = this.findBestPath(this.distance, this.nodesLeft); this.updateDistanceAndPrevious(this.bestPath); this.visited[this.bestPath] = 1; } this.getResults(); } private function somethingLeft(ourVisited:Array):Boolean { for (var i = 0; i < this.numberOfNodes; i++) { if (!(ourVisited[i])) { return true; } } return false; } private function nodesNotVisited(ourVisited:Array):Array { var selectedArray = new Array(); for (var i = 0; i < this.numberOfNodes; i++) { if (!(ourVisited[i])) { selectedArray.push(i); } } return selectedArray; } private function findBestPath(ourDistance:Array, ourNodesLeft:Array):Number { var bestPath = this.infiniteDistance; var bestNode = 0; for (var i = 0; i < ourNodesLeft.length; i++) { if (ourDistance[ourNodesLeft[i]] < bestPath) { bestPath = ourDistance[ourNodesLeft[i]]; bestNode = ourNodesLeft[i]; } } return bestNode; } private function updateDistanceAndPrevious(ourBestPath:Number):Void { for (var i = 0; i < this.numberOfNodes; i++) { if (!(this.map[ourBestPath][i] == this.infiniteDistance) || (this.map[ourBestPath][i] == 0)) { if ((this.distance[ourBestPath] + this.map[ourBestPath][i]) < this.distance[i]) { this.distance[i] = this.distance[ourBestPath] + this.map[ourBestPath][i]; this.previousNode[i] = ourBestPath; } } } } private function getResults():Void { var ourShortestPath = new Array(); for (var i = 0; i < this.numberOfNodes; i++) { ourShortestPath[i] = new Array(); var endNode = null; var currNode = i; ourShortestPath[i].push(i); while(endNode != this.startNode) { ourShortestPath[i].push(this.previousNode[currNode]); endNode = this.previousNode[currNode]; currNode = this.previousNode[currNode]; } ourShortestPath[i].reverse(); trace("---------------------------------------"); trace("The shortest distance from the startNode: "+this.startNode+ ", to node "+i+": is -> "+this.distance[i]); trace("The shortest path from the startNode: "+this.startNode+ ", to node "+i+": is -> "+ourShortestPath[i]); trace("---------------------------------------"); } } } ====Usage Example==== //Using a double scripted array as an adjacency matrix rowZero = new Array(0, 1000000, 1000000, 1000000, 5, 12); rowOne = new Array(15, 0, 9, 1000000, 1000000, 1000000); rowTwo = new Array(1000000, 1000000, 0, 5, 1000000, 1000000); rowThree = new Array(1000000, 2, 1000000, 0, 1000000, 1000000); rowFour = new Array(1000000, 1000000, 10, 1000000, 0, 4); rowFive = new Array(1000000, 1000000, 17, 20, 1000000, 0); ourMap = new Array(rowZero, rowOne, rowTwo, rowThree, rowFour, rowFive); var dijkstra = new Dijkstra(ourMap, 0, 1000000); dijkstra.findShortestPath(); ====Done Usage Example====
Python
import sys infinity = sys.maxint - 1 class Vertex(object): """A vertex in a graph, using adjacency list. 'edges' is a sequence or collection of tuples (edges), the first element of which is a name of a vertex and the second element is the distance to that vertex. 'name' is a unique identifier for each vertex, like a city name, an integer, a tuple of coordinates...""" def __init__(self, name, edges): self.name = name self.edges = edges def ShortestPath(graph, source, dest): """Returns the shortest distance from source to dest and a list of traversed vertices, using Dijkstra's algorithm. Assumes the graph is connected.""" distances = {} names = {} path = [] for v in graph: distances[v.name] = infinity # Initialize the distances names[v.name] = v # Map the names to the vertices they represent distances[source.name] = 0 # The distance of the source to itself is 0 dist_to_unknown = distances.copy() # Select the next vertex to explore from this dict last = source while last.name != dest.name: # Select the next vertex to explore, which is not yet fully explored and which # minimizes the already-known distances. next = names[ min( [(v, k) for (k, v) in dist_to_unknown.iteritems()] )[1] ] for n, d in next.edges: # n is the name of an adjacent vertex, d is the distance to it distances[n] = min(distances[n], distances[next.name] + d) if n in dist_to_unknown: dist_to_unknown[n] = distances[n] last = next if last.name in dist_to_unknown: # Delete the completely explored vertex path.append(last.name) del dist_to_unknown[next.name] return distances[dest.name], path
PHP
<?PHP class Dijkstra { var $visited = array(); var $distance = array(); var $previousNode = array(); var $startnode =null; var $map = array(); var $infiniteDistance = 0; var $numberOfNodes = 0; var $bestPath = 0; var $matrixWidth = 0; function Dijkstra(&$ourMap, $infiniteDistance) { $this -> infiniteDistance = $infiniteDistance; $this -> map = &$ourMap; $this -> numberOfNodes = count($ourMap); $this -> bestPath = 0; } function findShortestPath($start,$to = null) { $this -> startnode = $start; for ($i=0;$i<$this -> numberOfNodes;$i++) { if ($i == $this -> startnode) { $this -> visited[$i] = true; $this -> distance[$i] = 0; } else { $this -> visited[$i] = false; $this -> distance[$i] = isset($this -> map[$this -> startnode][$i]) ? $this -> map[$this -> startnode][$i] : $this -> infiniteDistance; } $this -> previousNode[$i] = $this -> startnode; } $maxTries = $this -> numberOfNodes; $tries = 0; while (in_array(false,$this -> visited,true) && $tries <= $maxTries) { $this -> bestPath = $this->findBestPath($this->distance,array_keys($this -> visited,false,true)); if($to !== null && $this -> bestPath === $to) { break; } $this -> updateDistanceAndPrevious($this -> bestPath); $this -> visited[$this -> bestPath] = true; $tries++; } } function findBestPath($ourDistance, $ourNodesLeft) { $bestPath = $this -> infiniteDistance; $bestNode = 0; for ($i = 0,$m=count($ourNodesLeft); $i < $m; $i++) { if($ourDistance[$ourNodesLeft[$i]] < $bestPath) { $bestPath = $ourDistance[$ourNodesLeft[$i]]; $bestNode = $ourNodesLeft[$i]; } } return $bestNode; } function updateDistanceAndPrevious($obp) { for ($i=0;$i<$this -> numberOfNodes;$i++) { if( (isset($this->map[$obp][$i])) && (!($this->map[$obp][$i] == $this->infiniteDistance) || ($this->map[$obp][$i] == 0 )) && (($this->distance[$obp] + $this->map[$obp][$i]) < $this -> distance[$i]) ) { $this -> distance[$i] = $this -> distance[$obp] + $this -> map[$obp][$i]; $this -> previousNode[$i] = $obp; } } } function printMap(&$map) { $placeholder = ' %' . strlen($this -> infiniteDistance) .'d'; $foo = ''; for($i=0,$im=count($map);$i<$im;$i++) { for ($k=0,$m=$im;$k<$m;$k++) { $foo.= sprintf($placeholder, isset($map[$i][$k]) ? $map[$i][$k] : $this -> infiniteDistance); } $foo.= "\n"; } return $foo; } function getResults($to = null) { $ourShortestPath = array(); $foo = ''; for ($i = 0; $i < $this -> numberOfNodes; $i++) { if($to !== null && $to !== $i) { continue; } $ourShortestPath[$i] = array(); $endNode = null; $currNode = $i; $ourShortestPath[$i][] = $i; while ($endNode === null || $endNode != $this -> startnode) { $ourShortestPath[$i][] = $this -> previousNode[$currNode]; $endNode = $this -> previousNode[$currNode]; $currNode = $this -> previousNode[$currNode]; } $ourShortestPath[$i] = array_reverse($ourShortestPath[$i]); if ($to === null || $to === $i) { if($this -> distance[$i] >= $this -> infiniteDistance) { $foo .= sprintf("no route from %d to %d. \n",$this -> startnode,$i); } else { $foo .= sprintf('%d => %d = %d [%d]: (%s).'."\n" , $this -> startnode,$i,$this -> distance[$i], count($ourShortestPath[$i]), implode('-',$ourShortestPath[$i])); } $foo .= str_repeat('-',20) . "\n"; if ($to === $i) { break; } } } return $foo; } } // end class ?>
Usage Example
<?php // I is the infinite distance. define('I',1000); // Size of the matrix $matrixWidth = 20; // $points is an array in the following format: (router1,router2,distance-between-them) $points = array( array(0,1,4), array(0,2,I), array(1,2,5), array(1,3,5), array(2,3,5), array(3,4,5), array(4,5,5), array(4,5,5), array(2,10,30), array(2,11,40), array(5,19,20), array(10,11,20), array(12,13,20), ); $ourMap = array(); // Read in the points and push them into the map for ($i=0,$m=count($points); $i<$m; $i++) { $x = $points[$i][0]; $y = $points[$i][1]; $c = $points[$i][2]; $ourMap[$x][$y] = $c; $ourMap[$y][$x] = $c; } // ensure that the distance from a node to itself is always zero // Purists may want to edit this bit out. for ($i=0; $i < $matrixWidth; $i++) { for ($k=0; $k < $matrixWidth; $k++) { if ($i == $k) $ourMap[$i][$k] = 0; } } // initialize the algorithm class $dijkstra = new Dijkstra($ourMap, I,$matrixWidth); // $dijkstra->findShortestPath(0,13); to find only path from field 0 to field 13... $dijkstra->findShortestPath(0); // Display the results echo '<pre>'; echo "the map looks like:\n\n"; echo $dijkstra -> printMap($ourMap); echo "\n\nthe shortest paths from point 0:\n"; echo $dijkstra -> getResults(); echo '</pre>'; ?>
Visual Basic
Option Explicit Const nodeCount As Integer = 9 'number of nodes - 1 Type DijkEdge weight As Integer 'distance from vertices that it is connected to destination As Integer 'name of vertice that it is connected to End Type Type Vertex connections(nodeCount) As DijkEdge 'hold information above for each connection numConnect As Integer 'number of connections - 1 distance As Integer 'distance from all other vertices isDead As Boolean 'distance calculated name As Integer 'name of vertice End Type Public Sub dijkstra_shortest_Path() Const infinity As Integer = 15000 'number that is larger than max distance Dim i As Integer 'loop counter Dim j As Integer 'loop counter Dim sourceP As Integer 'point to determine distance to from all nodes Dim inputData As String 'temp variable to ensure good data enterred Dim graph(nodeCount) As Vertex 'all inforamtion for each point (see Vertex declaration above) Dim nextP As Integer 'closest point that is not dead Dim min As Integer 'distance of closest point not dead Dim outString As String 'string to display the output Dim goodSource As Boolean 'user enters source point data and ensured that it is correct Do goodSource = True inputData = (InputBox("What is the source point: ", "Source Point between: 0 & " & nodeCount)) If IsNumeric(inputData) Then sourceP = CInt(inputData) If sourceP > nodeCount Or sourceP < 0 Then MsgBox "Source point must be between 0 & " & nodeCount & "." goodSource = False End If Else MsgBox "Source point must be numeric and be between 0 & " & nodeCount & "." goodSource = False End If Loop While Not goodSource 'get data so we can analyze the distances Call populateGraph(graph) 'set default values to not dead and distances to infinity (unless distance is to itself) For i = 0 To nodeCount If graph(i).name = sourceP Then graph(i).distance = 0 graph(i).isDead = False Else: graph(i).distance = infinity graph(i).isDead = False End If Next i For i = 0 To nodeCount min = infinity + 1 'determine closest point that is not dead For j = 0 To nodeCount If Not graph(j).isDead And graph(j).distance < min Then nextP = j min = graph(j).distance End If Next j 'calculate distances from the closest point & to all of its connections For j = 0 To graph(nextP).numConnect If graph(graph(nextP).connections(j).destination).distance > graph(nextP).distance + graph(nextP).connections(j).weight Then graph(graph(nextP).connections(j).destination).distance = graph(nextP).distance + graph(nextP).connections(j).weight End If Next j 'kill the value we just looked at so we can get the next point graph(nextP).isDead = True Next i 'display the distance from the source point to all other points outString = "" For i = 0 To nodeCount outString = outString & "The distance between nodes " & sourceP & " and " & i & " is " & graph(i).distance & vbCrLf Next i MsgBox outString End Sub
Example Data for testing
Private Sub populateGraph(vertexMatrix() As Vertex) 'get data into graph matrix to determine distance from all points Dim i As Integer Dim j As Integer '0 connections vertexMatrix(0).name = 0 vertexMatrix(0).numConnect = 3 vertexMatrix(0).connections(0).destination = 1 vertexMatrix(0).connections(1).destination = 2 vertexMatrix(0).connections(2).destination = 6 vertexMatrix(0).connections(3).destination = 7 vertexMatrix(0).connections(0).weight = 10 vertexMatrix(0).connections(1).weight = 15 vertexMatrix(0).connections(2).weight = 30 vertexMatrix(0).connections(3).weight = 50 '1 connections vertexMatrix(1).name = 1 vertexMatrix(1).numConnect = 3 vertexMatrix(1).connections(0).destination = 0 vertexMatrix(1).connections(1).destination = 3 vertexMatrix(1).connections(2).destination = 4 vertexMatrix(1).connections(3).destination = 9 vertexMatrix(1).connections(0).weight = 10 vertexMatrix(1).connections(1).weight = 16 vertexMatrix(1).connections(2).weight = 5 vertexMatrix(1).connections(3).weight = 40 '2 connections vertexMatrix(2).name = 2 vertexMatrix(2).numConnect = 3 vertexMatrix(2).connections(0).destination = 0 vertexMatrix(2).connections(1).destination = 7 vertexMatrix(2).connections(2).destination = 8 vertexMatrix(2).connections(3).destination = 9 vertexMatrix(2).connections(0).weight = 15 vertexMatrix(2).connections(1).weight = 33 vertexMatrix(2).connections(2).weight = 18 vertexMatrix(2).connections(3).weight = 60 '3 connections vertexMatrix(3).name = 3 vertexMatrix(3).numConnect = 1 vertexMatrix(3).connections(0).destination = 1 vertexMatrix(3).connections(1).destination = 4 vertexMatrix(3).connections(0).weight = 16 vertexMatrix(3).connections(1).weight = 22 '4 connections vertexMatrix(4).name = 4 vertexMatrix(4).numConnect = 2 vertexMatrix(4).connections(0).destination = 1 vertexMatrix(4).connections(1).destination = 3 vertexMatrix(4).connections(2).destination = 5 vertexMatrix(4).connections(0).weight = 5 vertexMatrix(4).connections(1).weight = 22 vertexMatrix(4).connections(2).weight = 30 '5 connections vertexMatrix(5).name = 5 vertexMatrix(5).numConnect = 0 vertexMatrix(5).connections(0).destination = 4 vertexMatrix(5).connections(0).weight = 30 '6 connections vertexMatrix(6).name = 6 vertexMatrix(6).numConnect = 1 vertexMatrix(6).connections(0).destination = 0 vertexMatrix(6).connections(1).destination = 7 vertexMatrix(6).connections(0).weight = 30 vertexMatrix(6).connections(1).weight = 40 '7 connections vertexMatrix(7).name = 7 vertexMatrix(7).numConnect = 3 vertexMatrix(7).connections(0).destination = 0 vertexMatrix(7).connections(1).destination = 2 vertexMatrix(7).connections(2).destination = 8 vertexMatrix(7).connections(3).destination = 6 vertexMatrix(7).connections(0).weight = 50 vertexMatrix(7).connections(1).weight = 33 vertexMatrix(7).connections(2).weight = 3 vertexMatrix(7).connections(3).weight = 40 '8 connections vertexMatrix(8).name = 8 vertexMatrix(8).numConnect = 1 vertexMatrix(8).connections(0).destination = 2 vertexMatrix(8).connections(1).destination = 7 vertexMatrix(8).connections(0).weight = 18 vertexMatrix(8).connections(1).weight = 3 '9 connections vertexMatrix(9).name = 9 vertexMatrix(9).numConnect = 1 vertexMatrix(9).connections(0).destination = 1 vertexMatrix(9).connections(1).destination = 2 vertexMatrix(9).connections(0).weight = 40 vertexMatrix(9).connections(1).weight = 60 End Sub